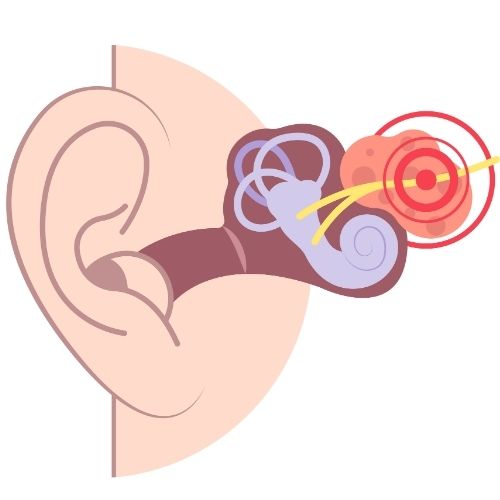
The human ear is a complex organ responsible for hearing and balance, and it can be affected by a variety of conditions. This article delves into common ear conditions, their symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies.
1. Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection)
Overview:
Otitis media is an infection or inflammation of the middle ear, often associated with fluid accumulation behind the eardrum.
Symptoms:
- Ear pain
- Hearing loss
- Fluid drainage from the ear
- Fever
- Irritability in children
Causes:
- Bacterial or viral infections, often following a cold or respiratory infection.
- Allergies and sinus infections can also contribute.
Diagnosis:
A healthcare provider typically diagnoses otitis media through a physical exam, checking for fluid in the ear with an otoscope.
Treatment:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
- Pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen or acetaminophen).
- In severe cases, a myringotomy (small incision in the eardrum) may be performed to drain fluid.
Prevention:
- Vaccination (e.g., pneumococcal vaccine).
- Avoiding smoke exposure and practicing good hygiene.
2. Tinnitus
Overview:
Tinnitus is the perception of noise or ringing in the ears, often occurring with hearing loss.
Symptoms:
- Ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds in the ears.
- The sounds may vary in volume and can be continuous or intermittent.
Causes:
- Exposure to loud noises, age-related hearing loss, ear infections, and certain medications (ototoxic drugs).
Diagnosis:
A thorough hearing examination and medical history review help determine the cause of tinnitus.
Treatment:
- Sound therapy (white noise machines).
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT).
- In some cases, hearing aids can be beneficial.
Prevention:
- Protecting ears from loud noises (earplugs, earmuffs).
- Regular hearing check-ups, especially for those exposed to high noise levels.
3. Hearing Loss
Overview:
Hearing loss can be conductive (related to outer/middle ear problems), sensorineural (inner ear or auditory nerve issues), or mixed.
Symptoms:
- Difficulty understanding speech.
- Frequently asking others to repeat themselves.
- Turning up the volume on devices.
Causes:
- Aging, noise exposure, genetic factors, infections, and ototoxic medications.
Diagnosis:
Audiometric tests conducted by an audiologist assess the degree and type of hearing loss.
Treatment:
- Hearing aids or cochlear implants for sensorineural loss.
- Surgery for conductive hearing loss, if applicable.
Prevention:
- Avoiding excessive noise exposure.
- Regular hearing assessments.
4. Meniere’s Disease
Overview:
Meniere’s disease is a chronic inner ear condition characterized by episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness in the ear.
Symptoms:
- Severe dizziness or vertigo attacks.
- Fluctuating hearing loss.
- Tinnitus.
- Pressure or fullness in the affected ear.
Causes:
The exact cause is unknown, but it may be related to abnormal fluid accumulation in the inner ear.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis involves clinical history, audiometric tests, and possibly imaging studies to rule out other conditions.
Treatment:
- Dietary changes (low salt, avoiding caffeine).
- Diuretics to reduce fluid retention.
- Vestibular rehabilitation therapy for balance issues.
- In severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
Prevention:
While there is no definitive prevention, managing stress and maintaining a healthy diet can help.
5. Earwax Buildup (Cerumen Impaction)
Overview:
Earwax (cerumen) is a natural substance produced by glands in the ear canal, but excessive buildup can cause blockage.
Symptoms:
- Earache or discomfort.
- Hearing loss.
- Itching in the ear canal.
- Ringing in the ears.
Causes:
- Overproduction of earwax, use of cotton swabs that push wax deeper, or ear canal shape.
Diagnosis:
A healthcare provider can easily diagnose cerumen impaction during an ear examination.
Treatment:
- Removal by a healthcare professional using suction or special instruments.
- Over-the-counter ear drops to soften wax.
Prevention:
- Avoid inserting objects into the ear canal.
- Regular check-ups to manage earwax levels.
6. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Overview:
This condition occurs when the Eustachian tube (which connects the middle ear to the back of the nose) fails to open properly, leading to pressure imbalances.
Symptoms:
- Ear fullness or pressure.
- Hearing changes.
- Discomfort during altitude changes (e.g., flying, driving in mountains).
Causes:
- Allergies, colds, sinus infections, or anatomical issues.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis is generally clinical, based on symptoms and history, with potential use of tympanometry to assess middle ear function.
Treatment:
- Decongestants or nasal sprays for temporary relief.
- In some cases, Eustachian tube balloon dilation surgery may be necessary.
Prevention:
- Managing allergies and colds effectively.
- Swallowing or yawning to help equalize pressure during altitude changes.

Ear conditions can significantly impact quality of life, but many are manageable with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Awareness of symptoms and preventive measures can help maintain ear health and address issues promptly. If you experience persistent symptoms related to your ears, consulting a healthcare professional is essential for appropriate care.